Creating a custom hook in react
In this article we will build a custom react hook which makes a fetch call to an endpoint every few 5 seconds. If the api call fails then after every random number of seconds it will make that same call. Let’s also add a refresh method to it so that you can call and forcully refresh the data.
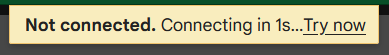
Guess where this will be helpful. This can used in web based email clients. You might have noticed in gmail, the mails are refreshed every few seconds, to load the latest set of received emails. And, in case you are not connected to the internet, it will show a banner at the top of the page which says - ‘Connecting in n seconds’, followed by a ‘Try now’ button. Something as shown below.
Here’s what the it(useFetch) will do:
- Pass GET url to the useFetch method
- Make a get call to that url every 5 seconds
- Allow users to call refresh and call api manually
- Make api calls in random intervals if api’s fail
- Return a isLoading flag to the user, based on which user can display different content in the component
- Return a remaining seconds counter to tell, how long it will wait to make the next call in case of failure
Something like this:
const [isLoading, remSeconds, refresh, data] = useFetch(url)
Let’s start with useFetch hook first
At first, create all the state variables required here, like isLoading, remSeconds, data. Also the constant time of 5 seconds in a variable.
function useFetch(url) {
const REFRESH_TIME = 5000;
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
const [remSeconds, setRemSeconds] = useState(0);
const [data, setData] = useState();
return [isLoading, remSeconds, refresh, data];
}
export default useFetch;Will also write a function which returns random time between 10 and 20 seconds that is used in case of failure.
function RandomSeconds() {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 10;
}Now let’s write the core functionality, the refresh function.
We need a timer object to track the time since last call. Initially when the refresh is called we need to clear the timer, set isLoading flag to true and also set the remaining seconds to 0. Then make the fetch call using the url. If the fetch was successfull then update the data in the data state, set loading flag to false and then start a timer to call the refresh function again after 5 seconds. If the fetch call fails, then in a similar way, start a timer with random number of seconds and call the refresh function.
let timer;
function refresh() {
clearTimeout(timer);
setIsLoading(true);
setRemSeconds(0);
fetch(url)
.then((response) => {
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
}
throw Error("Error with fetch call");
})
.then((response) => {
setData(response);
setIsLoading(false);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
refresh();
}, REFRESH_TIME);
})
.catch((error) => {
setIsLoading(true);
setData({});
let remTime = RandomSeconds();
setRemSeconds(remTime);
clearTimeout(timer); // TODO
timer = setTimeout(() => {
refresh();
}, remTime * 1000);
});
}The url passed by the user might be updated by the user frequently. So, in order to handle this scenario, lets write a useEffect which is called everytime the url is updated. The code should look something similar to this:
useEffect(() => {
setIsLoading(true);
setRemSeconds(0);
setData();
refresh();
}, [url]);So, the entire useFetch hook should look like this:
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
function useFetch(url) {
const REFRESH_TIME = 5000;
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
const [remSeconds, setRemSeconds] = useState(0);
const [data, setData] = useState();
function RandomSeconds() {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 10;
}
let timer;
function refresh() {
clearTimeout(timer);
setIsLoading(true);
setRemSeconds(0);
fetch(url)
.then((response) => {
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
}
throw Error("Error with fetch call");
})
.then((response) => {
setData(response);
setIsLoading(false);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
refresh();
}, REFRESH_TIME);
})
.catch((error) => {
setIsLoading(true);
setData({});
let remTime = RandomSeconds();
setRemSeconds(remTime);
clearTimeout(timer); // TODO
timer = setTimeout(() => {
refresh();
}, remTime * 1000);
});
}
useEffect(() => {
setIsLoading(true);
setRemSeconds(0);
setData();
refresh();
}, [url]);
return [isLoading, remSeconds, refresh, data];
}
export default useFetch;Now, let’s create a component that uses this hook.
import useFetch from "./Fetch";
export default function App() {
const [isLoading, remSeconds, refresh, data] = useFetch(
"https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users"
);
return (
<div>
{isLoading ? (
<div>
<div>Message: Data is loading</div>
<div>Remaining time: {remSeconds} seconds</div>
<div>
<input type="button" value="Refresh" onClick={refresh} />
</div>
</div>
) : (
<div>
<ul>
{data.map((val, i) => (
<li>
{val.name} ({val.username})
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}Here, if the api call is successfull, it will display a list of users. If it fails, it will display a message, with remaining seconds and a refresh button.
Note: The remaining seconds doesn’t update the time every one second, it just displays the total time remaning until next call.
Check this codesandbox link to play around with the code - link